서론
수술 중 발생하는 신경계 손상 여부를 감별하는 검사인 수술 중 신경계 감시검사(intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring, INM)는 신경외과, 정형외과 그리고 흉부외과 등 신경계 수술에서 이용되어 수술 중 신경계의 손상을 조기에 찾아서 수술 후의 합병증을 줄여주어 집도의가 수술을 안전하게 진행할 수 있도록 도움을 주는 매우 중요한 검사이다. 수술 중 신경계 감시 검사 중 유발전위 검사는 종류에 따라 시각유발전위(visual evoked potential, VEP), 청각유발전위(brainstem auditory evoked potential, BAEP), 운동유발전위(motor evoked potential, MEP), 감각유발전위(somatosensory evoked potential, SSEP), 자유 진행 및 유발 근전도 검사(running and triggered electromyography)로 분류된다.
시각유발전위(VEP)는 시각적 자극으로 인해 유발된 전위를 측정하는 검사로 시각 경로의 이상을 파악할 수 있다[1]. 시각 경로와 밀접한 수술 시에 발생할 수 있는 시각 경로 손상을 수술 시에 알고 수술 후 합병증을 최소화하기 위해 시각 유발 전위 검사를 이용할 수 있지만, 다른 수술 중 신경계 감시법보다 사용이 보편화되지 않았다. 그 이유는 시각 유발 전위 검사가 마취의 영향을 많이 받고, 파형의 재현성이 나쁘고, 자극 및 기록이 힘들기 때문이다. 그러나 21세기 들어 전 정맥 마취(total intravenous anesthesia, TIVA)를 통한 마취 방법의 발달, 발광 다이오드(light-emitting diode, LED) 방법 등을 이용한 시작 자극과 전기망막검사(electroretinography, ERG)의 기록 방법이 도입되면서 시각 유발 전위 파형의 기록이 더욱 정확해지며 수술 중신경계 감시로 사용되었다는 보고들이 있다[2–4]. 뇌하수체 종양이나 인후두종(craniopharyngioma)과 안장 옆 병변(parasellar lesion) 수술에서 시신경을 추적감시하기 위해 시각유발전위(VEP)를 이용할 수 있다. 하지만 시교차전 병변의 수술에서 많이 사용되며 보고되어 왔고, 아직 시교차 후의 병변에 대해서는 추가적인 연구가 진행 중이다.
이에 시각교차 부위와 전, 후 시각교차 부위의 병변을 갖고 있는 환자에서 VEP의 재현성이 좋았던 증례들을 보고하고자 한다.
증례
본 증례들에서 마취는 프로포폴(propofol)과 레미펜타닐(remifentanil)을 사용하여 완전정맥마취(TIVA)를 시행하였다. 수술중신경계감시는 운동유발전위(MEP), 체성감각유발전위(SSEP) 및 시각유발전위(VEP)를 시행하였으며, Xltek Protektor(Xltek Protektor 32, Natus Medical, Pleasanton, WI, USA) 장비를 이용하여 검사하였다.
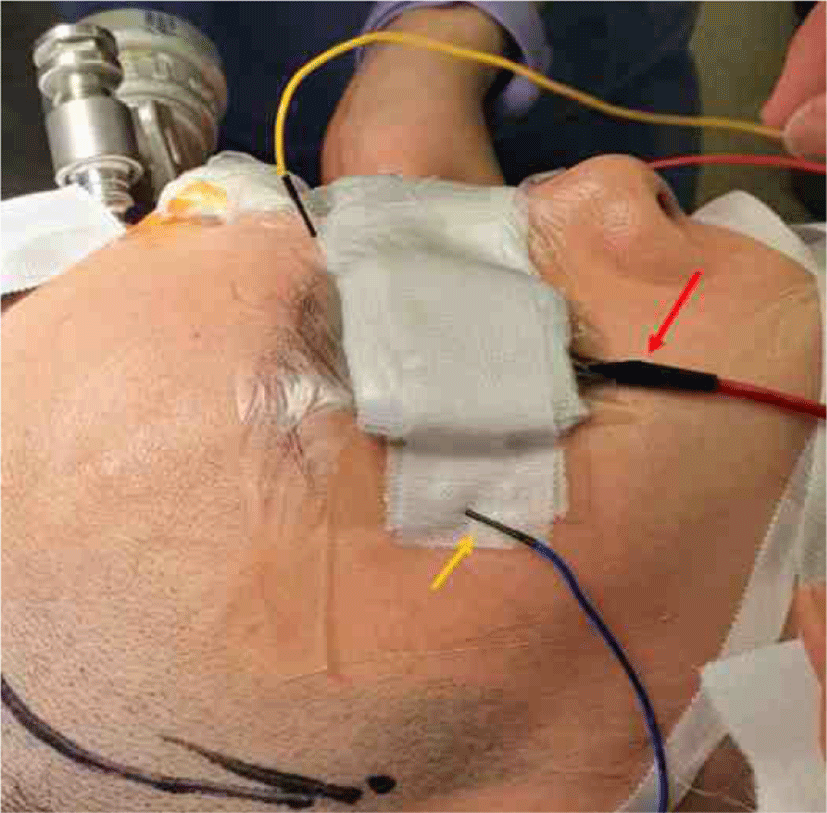
시각유발전위(VEP) 감시를 위한 빛 자극은 고글 안경을 통해 플래쉬(flash) 형태의 번쩍이는 발광 다이오드(LED) 자극을 반복해서 준다. 한쪽 눈씩 검사를 진행하며, 빛 자극의 빈도는 1.0 Hz이며, 주파수 폭(band-pass)은 high-pass filter는 200 Hz, low-pass filter는 20 Hz로 설정하고, 평균화 횟수는 50번으로 설정하였다. 기록전극은 Queen square 전극 부착법을 이용하여, 뒤통수점(inion)에서 5 cm 상방에 middle occipital (MO), 좌측으로 5 cm, 우측으로 5 cm 지점에 left occipital (LO), right occipital (RO)을 위치한다. Queen square system에 추가로 LO와 RO의 외측으로 5 cm 지점에 left temporal (LT), right temporal (RT)를 위치하였다. A1, A2는 기준전극으로 사용하였다.
망막(retina)에 빛 자극이 전달되는지 확인하기 위해 전기망막검사(ERG)를 같이 시행하였고, 전기망막검사(ERG)용 바늘 전극은 외측 눈구석(lateral canthus)에 피하로 삽입하였고, 기준 전극은 반대쪽 외측 눈구석(lateral canthus)에 삽입하였다(Fig. 1) [1,5]. 수술 중 시각유발전위(VEP)의 파형은 P100 진폭의 50%의 감소와 잠복기 지연의 여부 등을 확인하여 이상 여부를 판단하였다.
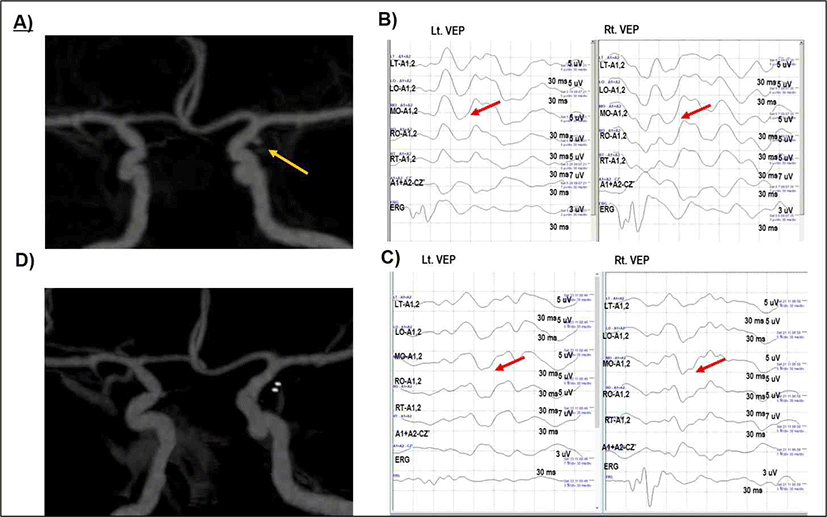
51세 여자가 수년 전부터 발생한 두통에 대한 원인 확인 위해 타원에서 시행한 뇌 자기공명 혈관영상(magnetic resonance angiography, MRA)에서 좌측 앞맥락동맥류(anterior choroidal artery aneurysm)가 의심되었고 본원 내원하였다. 본원에서 시행한 뇌 컴퓨터 단층 촬영 영상(computed tomography angiography, CTA)에서 좌측 앞맥락동맥(anterior choroidal artery) 기시부에 약 2 mm 크기로 소낭성 동맥류(saccular aneurysm)가 확인되었고(Fig. 2-A) 신경학적 검사상 이상 소견이 없었으며, 가족력상 아버지의 뇌출혈이 있었다. 동맥결찰술(aneurysm clipping)을 시행하였고, 수술 중 시각유발전위(VEP) 검사를 시행하였다. 수술 시행 전 전기망막검사(ERG)와 시각유발전위(VEP)의 기본 파형을 확인하였다. 전기망막검사(ERG)의 파형이 잘 유지되는 것으로부터 망막(retina)에 빛 자극이 전달되는지 확인할 수 있었고, 좌안과 우안 모두 P100 파형이 잘 확인되었다(Fig. 2-B). 수술 진행 중에도 양안의 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형은 잘 유지되었고, 파형의 재현성이 좋았다(Fig. 2-C). 수술 종료 전 확인한 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형도 양안 모두에서 잘 관찰되었다. 운동유발전위(MEP), 체성감각유발전위(SSEP) 상에서도 수술 중 파형의 유의한 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 수술 후 시행한 뇌 컴퓨터 단층 촬영 영상(CTA)으로 추적검사하였고, 동맥류가 소실된 것이 확인되었으며(Fig. 2-D), 환자는 특별한 부작용 없이 퇴원하였다. 수술 후 한달 경과 후 외래 내원하였고, 시력감소 및 시야장애의 호소는 없었다. 전시각교차(prechiasmatic lesion) 병변 환자에서 수술 시 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형이 잘 확인되고, 수술 중 재현성이 잘 유지된 것을 확인한 예이다.
40세 여자가 2차성 무월경 및 유루증 증상으로 시행한 뇌 자기공명 영상검사(magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)상 안장 위 침범을 동반한 20 mm 크기의 뇌하수체 거대선종(pituitray macroadenoma)이 확인되었다(Fig. 3-A). 3개월 간 도파민 작용제(cabergolin) 치료를 시행하였으나, 추적 뇌 자기 공명 영상 상에서 크기가 감소되지 않아 수술적 치료를 위해 본원 입원하였다. 시야 검사를 포함한 신경학적 검사상 이상 소견은 관찰되지 않았고, 시야 계측 검사(perimetry) 상에서도 시야 장애는 확인되지 않았다. 환자는 나비뼈 경유(transsphenoidal approach)하 선종 제거 수술을 시행하기로 하였고, 수술 중 시각유발전위(VEP) 감시를 시행하였다.
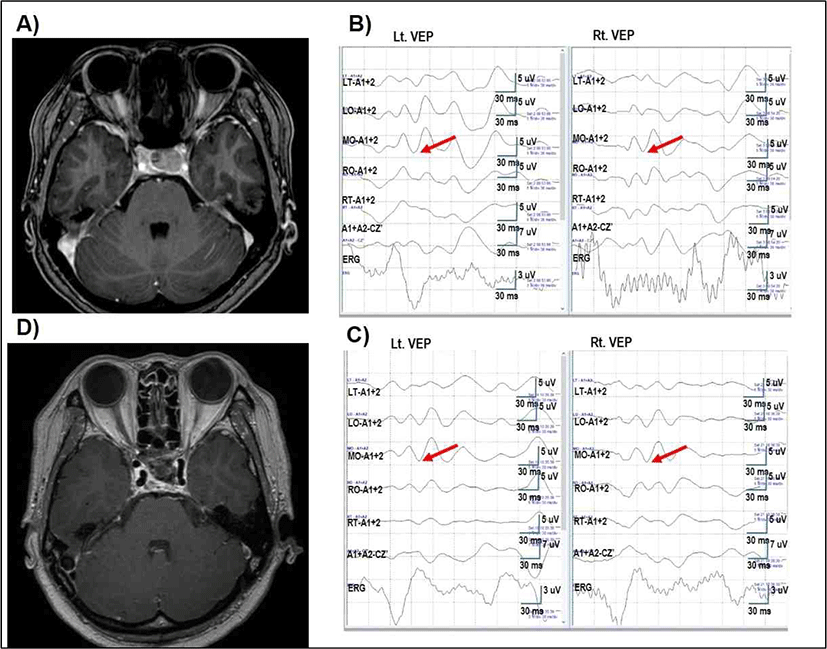
수술 시작 전 양안 모두에서 전기망막검사(ERG)와 시각유발전위(VEP)의 파형이 잘 확인되었고, 수술 중 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형은 재현성이 잘 유지되었으며(Fig. 3-B), 수술 종료 전 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형은 수술 시작 시와 뚜렷한 차이가 없는 것으로 확인하였다(Fig. 3-C). 수술 중 운동유발전위(MEP), 체성감각유발전위(SSEP) 추적 검사도 시행하였고, 수술 중 유의한 변화는 관찰되지 않았다.
수술 후 시행한 뇌 자기공명 영상검사(MRI)에서 그 크기감소를 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 3-D). 환자는 신경학적 변화 소견 및 특이 부작용 없이 퇴원하였으며, 이후 내분비내과에서 시행한 복합뇌하수체자극검사(칵테일검사, cocktail test)상에서 뇌하수체 기능 부전(hypopituitarism) 소견 보이지 않고, 호르몬 수치는 정상 범위임을 확인하였다. 또한 수술 3개월 후 시력검사 및 시야 계측 검사(perimetry) 추적관찰 상에서 시야 장애는 확인되지 않았다.
상기 증례는 시신경 교차 부위(chiasmatic lesion)에 병변을 보이는 환자에서 시각유발전위(VEP) 파형이 잘 확인되었고, 재현성이 잘 유지된 것을 확인한 증례이다.
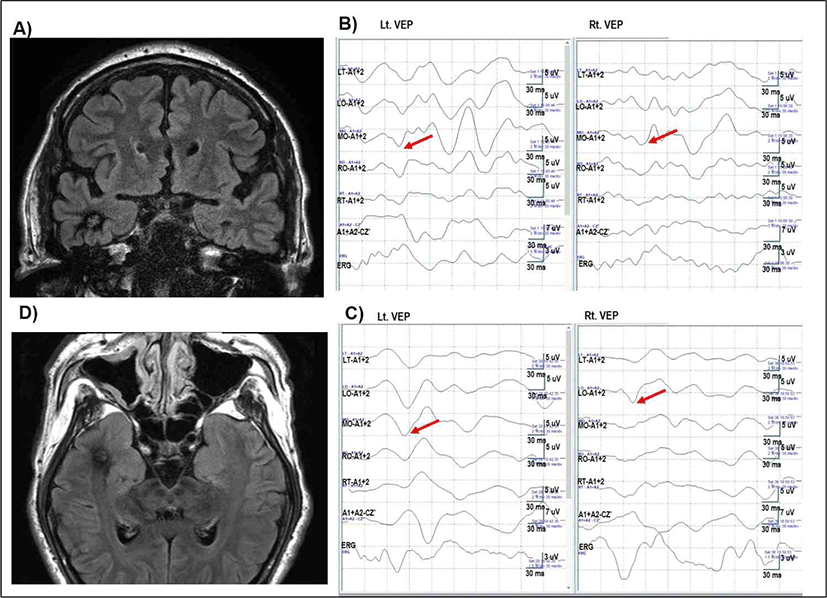
52세 남자 환자로 내원 13년 전부터 시작된 자동 운동성 발작(automotor seizure)으로 타원에서 항뇌전증약물 복용을 시작하였다(valproate 1,000 mg/day, carbamazepine 400 mg/day, lacosamide 100 mg/day, clobazam 10 mg/ day). 약물 복용함에도 발작 증상이 반복되었고, 수 차례의 교통사고가 있어 본원 신경과에 입원하여 난치성 뇌전증의 수술을 위한 지속적 뇌파 감시 시행하였다. 우측 앞측두엽에서 뇌전증 발작 지점(ictal onset)이 확인되었고, 다른 신경학적 검사상 이상 소견은 없었다. 뇌 자기공명 영상에서 우측 측두엽 앞쪽, 기저부에 해면상 기형 소견이 확인되었다(Fig. 4-A, 4-D). 증상성 우측 측두엽 뇌전증으로 진단하고, 우측 앞측두엽 및 편도해마 부분 절제술(right anterior temporal lobectomy and subtotal amygdalohippocampectomy)을 시행하였다. 마취는 프로포폴(propofol)과 레미펜타닐(remifentanil)을 사용하여 완전정맥마취(TIVA)를 시행하였다. 수술 시작 시 시각유발전위(VEP) 상(Fig. 4-B)에서 왼 눈 자극 시와 오른 눈 자극 시에 모두 LT, LO, MO, RO, RT에서 P100의 진폭이 확인되었다. 수술 종료 전 시각유발전위(VEP) 상에서도 수술 전과 P100, M wave 뚜렷한 차이는 확인되지 않았다(Fig. 4-C). 수술 중 함께 시행한 체성감각유발전위(SSEP), 운동유발전위(MEP) 검사에서 유의한 변화는 관찰되지 않았다. 환자 수술 후 특별한 합병증 호소도 없었고, 퇴원 후에도 수 개월에 한 번씩 발작 전구 증상이 있었으나, 지속시간은 이전보다 현저히 짧았다고 하였다.
고찰
시각유발전위(VEP)는 몇 가지 한계점들로 인해 그 유용성이 다른 수술 중 신경계 감시법에 비해 덜 확립되었다. 시각유발전위(VEP)는 근접 필드(near field) 방식으로 전위형성부위와 기록 부위가 근접하여 전위의 진폭 변화가 크고, 마취제의 종류나 마취의 정도에 따른 진폭의 변화가 있어 다른 유발 전위 검사들과 비교하였을 때 P100만을 이용하여 변화를 확인하기에 어려움이 있다. 현재까지 수술 중 시각유발전위(VEP) 감시는 주로 전시신경교차 부위에서 사용되었다. 시신경교차 부위와 후시신경교차 부위에서 사용한 보고들이 있기는 하나, 아직 유용성에 대해 확립되지는 못한 상태이다[6]. 한계점들을 보완하여 파형 기록을 보다 정확하게 하고, 판독의 용이성을 위해 본원에서는 시각유발전위(VEP) Queen Square법을 사용하고 있으며, 추가적으로 RT, LT를 부착하여 수술 중 감시를 하고 있다[5,7,8]. 또한 망막(retina)에 빛 자극이 전달되는지 확인하기 위해 전기망막검사(electroretinogram, ERG)를 함께 적용하고 있다[7].
시각유발전위(VEP) 판독은 잠복기 확인 후 진폭을 확인하는데, 진폭 감소, 반구 간 차이 비를 확인한다. Large positive peak 100 msec (p100), negative 75 msec (N75), negative 135 msec (N135)의 지표를 이용하여 판독하게 된다. 파형의 분석은 100–240 msec에서 발생하는 늦은 파형 부분(late component)을 관찰하였다. Wave III (P100)과 wave VII 사이에서 형성되는 “M” (IV-V-V0-VI) 형태의 polyphasic wave가 이전까지는 임상적 의미가 없는 것으로 생각되었으나, 본 증례보고에서는 이러한 형태를 유지하는 것이 시각유발전위(VEP) 검사 해석에 유용하였다.
시각유발전위(VEP) 확인 시에 M 형태의 wave를 확인함으로써 100 msec 전반과 250 msec 후반과의 관계와 함께, 100에서 250 msec 사이의 파형 관계를 확인하면서 진폭의 감소인 편평화(wave flattening), 파형의 잠복기 연장, 또는 파형 모양의 변화가 있는지 즉각적으로 알 수 있었다.
본 증례에서 양측 측두엽 전극을 추가 적용함으로써 시각유발전위(VEP)에서 시신경교차 부위와 후시신경교차의 차이를 구분하기 용이하였으며, 특히 증례 2, 3에서 검사자의 재현성을 높일 수 있었다. 하지만 이와 같은 병변 부위별 시각유발전위(VEP)의 차이는 수술 시작부터 나타나 수술 끝까지 유지되었고, 수술 중 특정 시각 경로 부위의 손상에 의한 시각유발전위(VEP)의 변화를 감지한 것은 아니다. 따라서 시각유발전위(VEP)를 이용한 수술중 신경계 감시 검사의 민감도를 높이기 위한 방법에 대한 연구가 필요하다.
