Case Report
반측안면경련 수술에서 뇌줄기청각유발전위 제1파형의 임상적 의미
백재승1,2,†
,
김용균1,2,†
,
김재림1,2
,
배효은1,2
,
박수련1,2
,
김기현1,2
,
서수연1,2,3
,
이정석3,*
,
서대원1,2,*
Clinical significance of wave I in brainstem auditory evoked potentials during microvascular decompression surgery for hemifacial spasm: a case report
Jae Seung Baek1,2,†
,
Yong Kyun Kim1,2,†
,
Jae Rim Kim1,2
,
Hyoeun Bae1,2
,
Soo Ryun Park1,2
,
Ki Hyun Kim1,2
,
Suyeon Seo1,2,3
,
Jung-Seok Lee3,*
,
Dae-Won Seo1,2,*
Author Information & Copyright ▼
1성균관대학교 의과대학 삼성서울병원 신경과학교실
1Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Neuroscience Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Neurology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
*Corresponding author: Jung-Seok Lee, Department of Neurology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju 63241, Korea, Tel: +82-64-754-8178, Fax: +82-64-727-3114, E-mail:
[email protected]
*Corresponding author: Dae-Won Seo, Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul 06351, Korea, Tel: +82-2-3410-3595, Fax: +82-2-3410-0052, E-mail:
[email protected]
© Copyright 2023 Korean Society of Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring. This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the
Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits
unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any
medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: Apr 12, 2023 ; Revised: May 20, 2023 ; Accepted: Jun 26, 2023
Published Online: Jun 30, 2023
ABSTRACT
Hemifacial spasm (HFS) is an involuntary contraction of muscles on one side of the face. It is caused by compression of the facial nerve by blood vessels. Microvascular decompression (MVD) is an effective treatment for HFS. However, complications such as hearing loss and dizziness may occur due to nerve deficits during surgery. To prevent this, neural monitoring is performed with brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs). In most hospitals, the presence or absence of BAEPs V waveform is used as an indicator for monitoring. Also, it tends to be intensively implemented only during the main procedure. In this report, we compare three cases in which there were differences in postoperative hearing complications depending on the presence of wave I. This suggests the importance of attention on wave I of BAEPs monitoring during MVD surgery and the need for acquiring wave I data until closing time as well during the main procedure.
Keywords: evoked potentials, auditory, brain stem; hemifacial spasm; microvascular decompression surgery
서론
얼굴의 한 쪽 근육이 불수의적으로 수축하는 신경 질환인 반측안면경련(hemifacial spasm)은 혈관이 얼굴 신경을 압박해 발생한다[1]. 이러한 증상을 완화시키기 위해서 미세혈관갑압술(microvascular decompression, MVD) 수술이 효과적으로 사용되고 있다[2]. 그러나, MVD 수술은 뇌간 및 관련 구조물을 손상시키는 위험성을 가지고 있어 청력 소실, 이명, 어지럼증, 또는 기타 신경 결손을 유발할 수 있다[3]. 따라서, MVD 수술 중 뇌줄기청각유발전위(brainstem auditory evoked potentials, BAEPs) 감시가 이러한 합병증을 예방하는 유용한 도구로 제안되고 있다. 그러나, 수 초간의 짧은 시간 동안 신경 손상이 유발될 수 있어서 대부분의 병원에서는 BAEPs wave V 파형의 유무를 감시의 지표로 사용한다. 또한 주요 수술 절차 중에만 집중적으로 시행하고 이후 주요 수술 절차 이후에는 소홀히 하는 경향이 있다. 본 증례는 BAEPs wave V 파형이 소실되었고, wave I 파형 유무에 따른 환자의 수술 후 합병증의 차이에 대해 논의하고, 메인 수술까지는 BAEPs 파형 변화가 없었다가 이후에 소실되었고 환자는 수술 후 청력 소실을 동반한 어지럼증이 생긴 것을 통해 메인 수술 이후에도 지속적인 감시가 필요함을 강조하고자 한다.
증례
1. 수술중 신경계 감시 방법
검사는 엑셀텍(Xltek Protektor 32, Natus Medical, Middleton, WI, USA) 장비를 이용해 시행하였고, 수술 중 신경계감시로 뇌줄기청각유발전위, 신경흥분도검사를 진행하였다. 청각유발전위 자극의 빈도는 43.9 Hz, 기록은 활동기록전극은 A1과 A2 전극, 참고기록전극은 Cz 전극으로 하였다. 신경흥분도검사는 자극의 강도는 10–30 mA, 자극 기간은 0.2 msec, 단일 펄스 방식으로 자극하였고, 기록은 안면 신경의 지배를 받는 이마근(frontalis), 안륜근(orbicularis oculi), 구륜근(orbicularis oris), 턱근(mentalis)에서 하였다.
2. Case 1
1) 임상소견
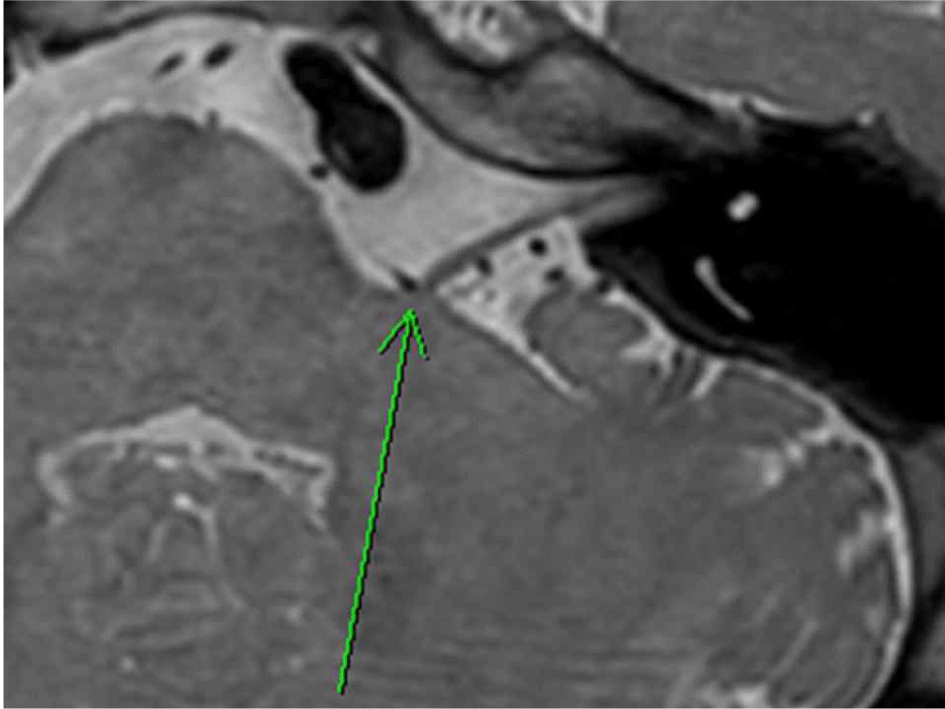
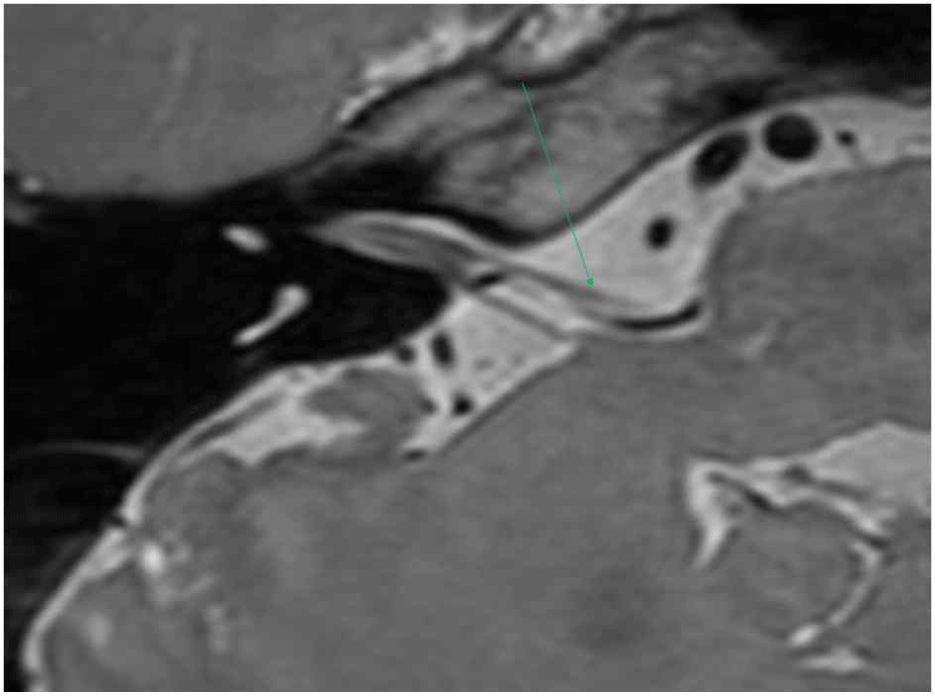
6년 전부터 좌측 안면 경련 증상을 호소한 60세 여자에 대해 수술적 치료가 결정되었다. 환자는 수술 결정 1년 전부터 4회에 걸친 보톡스 주사 치료를 받았으나 증상이 지속되어 미세혈관감압 수술을 진행하기로 하였다. 신경학적 진찰 상 눈 주위 근육과 입 주위 근육의 연합운동 현상이 관찰되었으나 안면마비는 보이지 않았다. 본원에서 시행한 뇌자기공명영상에서 좌측 전하소뇌동맥으로 인해 안면 신경의 기시부에서 안면 신경의 국소적인 압박이 확인되었다(Fig. 1). 안면신경 수술 전 제반 검사에서 순음청력검사 및 청각유발전위검사 상에는 이상 소견이 없었으나, 신경흥분도검사에서 안면신경 상하 분지 간의 측면전파반응(lateral spread response)이 관찰되었다.
Fig. 1.
Preoperative axial MRI.
Left anterior inferior cerebellar artery (arrow) causing focal compression of the root exit zone of the ipsilateral facial nerve.
Download Original Figure
2) 수술중신경계감시
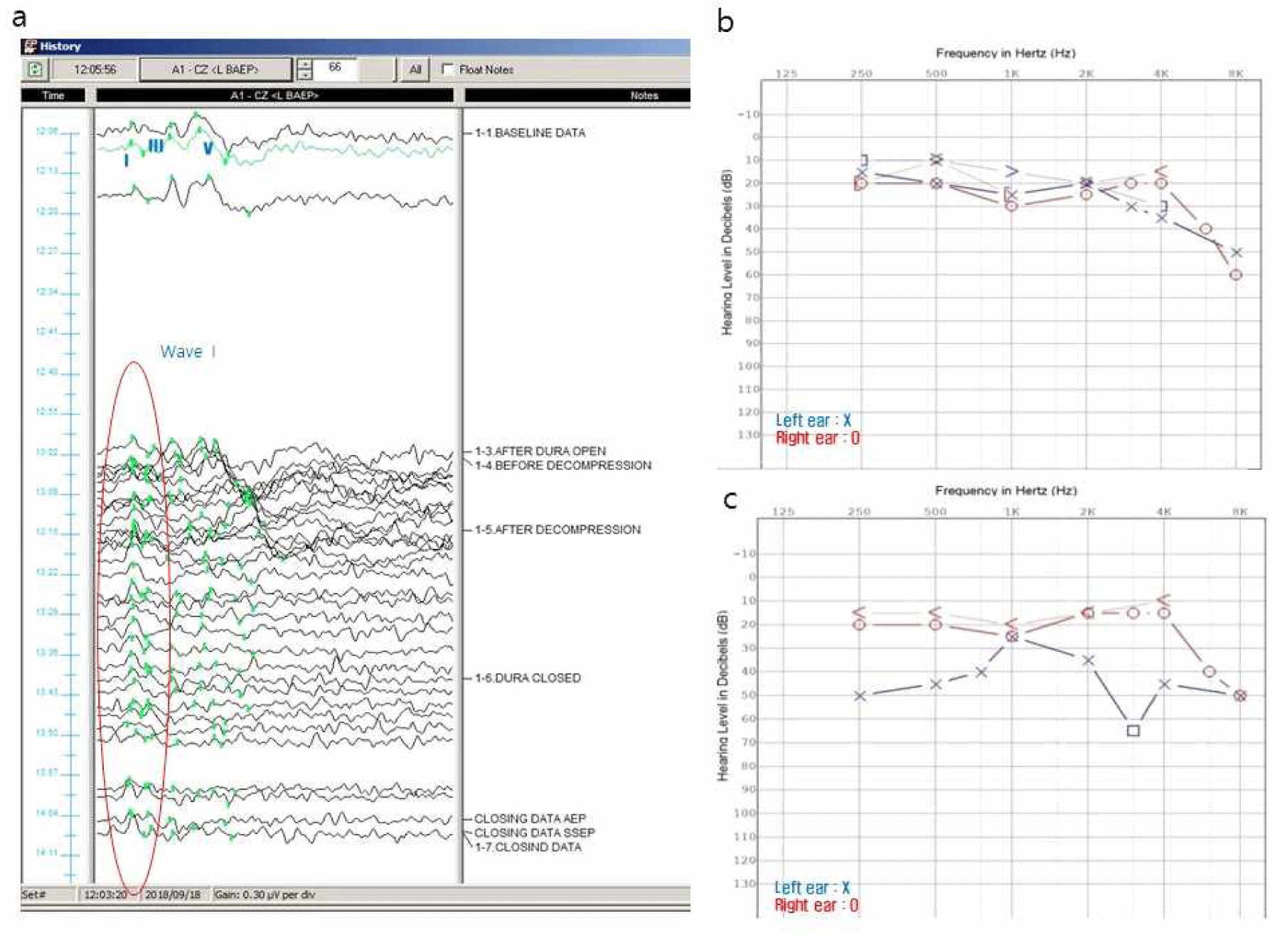
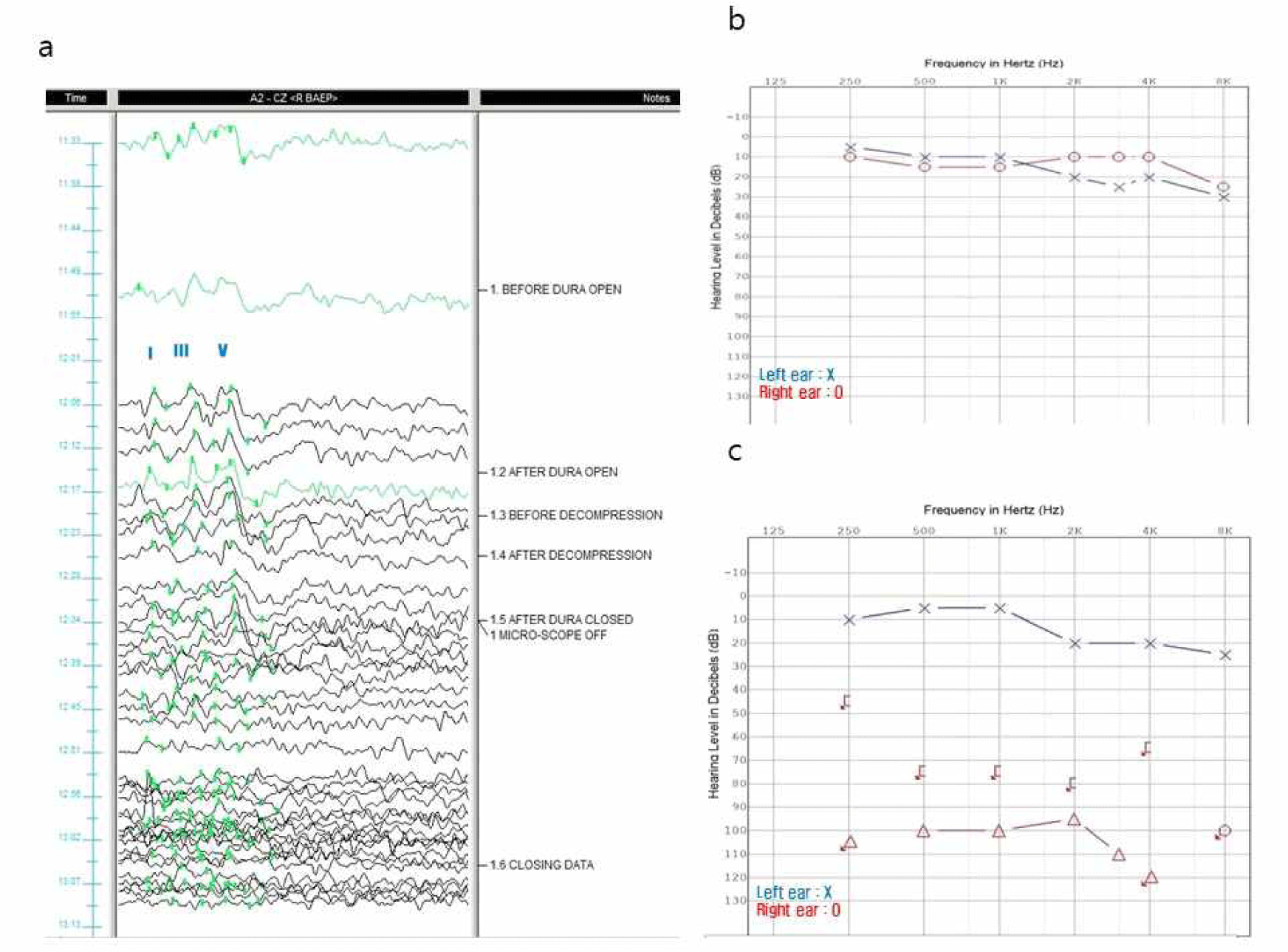
감시를 진행하며 좌측 뇌줄기청각유발전위에서는 wave I을 제외한 모든 파형이 서서히 소실되었다. 결국 종료 시점에 다른 파형들은 회복되지 않고 wave I만 남아 있는 상태로 수술을 마쳤다(Fig. 2-a). 측면전파반응은 안면신경의 감압 이후에 사라졌다.
Fig. 2.
Clinical data of case 1.
(a) Stacked waves of left brainstem auditory evoked potentials (Lt. BAEPs). All BAEPs waves except wave I are lost (circle) during the main procedure. (b) Pre-operative pure tone audiometry (PTA). Pre-op PTA is normal. (c) Post-operative PTA. The hearing level is increased by 20–30 dB in the left at 250, 500, 2,000, and 4,000 Hz.
Download Original Figure
3) 결과
환자는 수술 후 좌측 안면 경련 증상은 호전되었으나, 수술 당일 마취에서 회복된 후부터 좌측 청력 저하를 호소하였다. 수술 전 시행한 검사와 비교하여 수술 사흘 뒤에 진행한 순음청력검사(pure tone audiometry)에서 좌측 250–500 Hz와 2,000–4,000 Hz 영역에서 청력 역치(hearing level)가 20–30 dB 정도 증가되었다(Fig. 2-b and 2-c).
3. Case 2
1) 임상소견
4년 전부터 우측 눈떨림 증세를 호소한 60세 여자 환자에 대해 수술적 치료가 결정되었다. 신경학적 진찰 상 안면마비는 없었으나 우측 안면부에 연합운동 현상이 관찰되었다. 본원에서 시행한 뇌자기공명영상에서 우측 전하소뇌동맥과 작은 정맥으로 인해 안면 신경의 기시부에서 안면 신경의 국소적인 압박이 확인되었다(Fig. 3). 신경흥분도검사에서 안면신경 상하 분지 간의 측면전파반응이 관찰되었다. 수술 전에 시행한 순음청력검사 및 뇌줄기청각유발전위 검사는 정상 소견이었다.
Fig. 3.
Preoperative axial MRI.
Right anterior inferior cerebellar artery (arrow) and a small vein are in close proximity to root exit zone of the ipsilateral facial nerve.
Download Original Figure
2) 수술중신경계감시
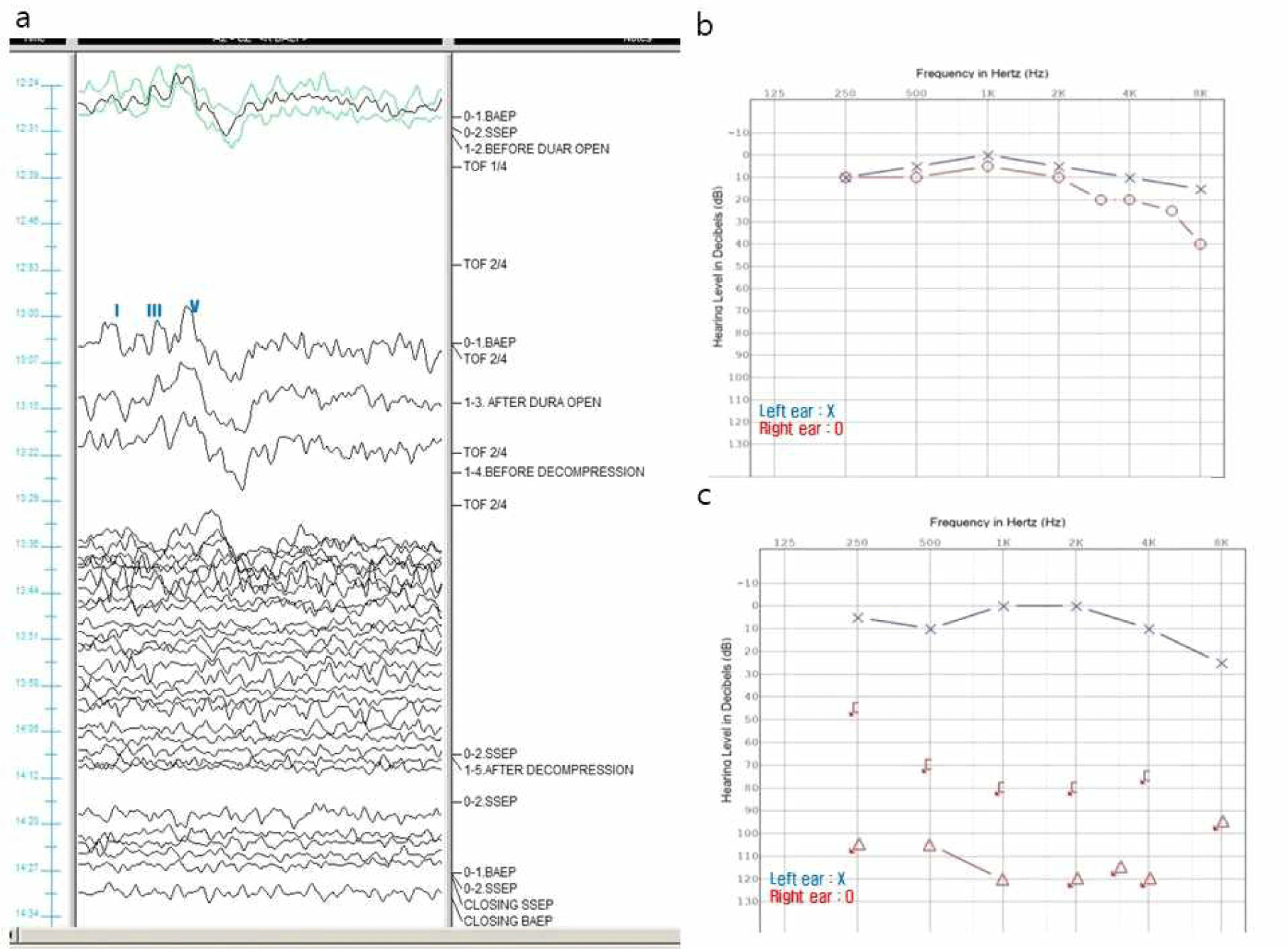
감시를 진행하며 우측 뇌줄기청각유발전위에서 wave I부터 wave V까지 모든 파형이 소실되었고 수술 종료 시점까지도 회복되지 않았다(Fig. 4-a). 측면전파반응은 안면신경의 감압 이후에 사라졌다.
Fig. 4.
Clinical data of case 2.
(a) Stacked waves of right brainstem auditory evoked potentials (Rt. BAEPs). All BAEPs waves including wave I are lost during the main procedure. (b) Pre-operative pure tone audiometry (PTA). Pre-op PTA is normal. (c) Post-operative PTA. Significant hearing loss is observed in all frequency domains on the right side.
Download Original Figure
3) 결과
환자는 수술 당일 마취에서 회복된 후부터 우측 귀의 청력 소실과 어지럼증을 호소하였다. 안면경련 증상은 호전되었으나 수술 8일 후에 진행한 순음청력검사상 우측의 모든 주파수 영역에서 현저한 청력 저하를 보였다(Fig. 4-b and 4-c).
4. Case 3
1) 임상소견
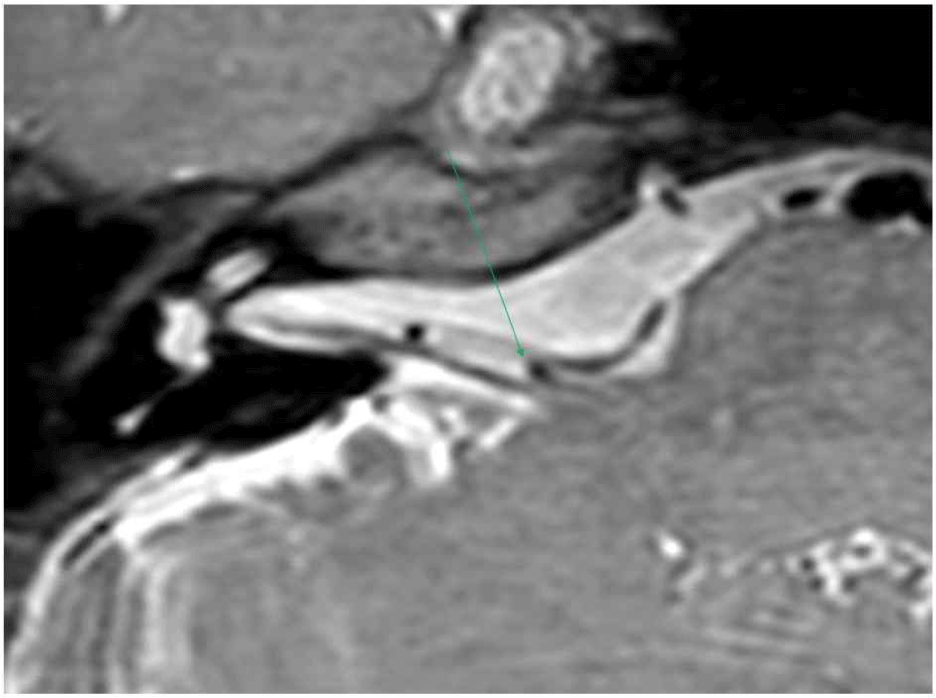
52세 여자 환자가 2년전부터 시작된 우측 눈 주변 부위 경련 증상에 대한 수술적 치료를 위해 내원하였다. 신경학적 진찰 상 눈 주위 근육과 입 주위 근육의 연합운동 현상이 관찰되었으나 안면마비는 보이지 않았다. 본원에서 시행한 뇌자기공명영상에서 우측 전하소뇌동맥으로 인해 안면 신경의 기시부에서 안면 신경의 국소적인 압박이 확인되었다(Fig. 5). 수술 전에 시행한 순음청력검사 및 뇌줄기청각유발전위에서는 이상 소견이 없었으나 신경흥분도검사에서 안면신경 상하 분지 간의 측면전파반응이 관찰되었다.
Fig. 5.
Preoperative axial MRI.
Right anterior inferior cerebellar artery (arrow) causing compression of the root exit zone of the ipsilateral facial nerve.
Download Original Figure
2) 수술중신경계감시
뇌줄기청각유발전위에서는 주요 술기(혈관 감압)를 진행하는 동안에는 유의한 파형 변화가 나타나지 않았으나 수술 마무리 단계에서 경막을 닫은 이후에 우측 자극에 대한 반응이 모두 소실되어 종료 시점까지도 모든 파형이 회복되지 않았다(Fig. 6-a). 측면전파반응은 안면신경의 감압 이후에 사라졌다.
Fig. 6.
Clinical data of case 3.
(a) Stack waves of right brainstem auditory evoked potentials (Rt. BAEPs). All BAEPs waves including Wave I are lost after the main procedure. (b) Pre-operative pure tone audiometry (PTA). Pre-op PTA is normal. (c) Post-operative PTA. Significant hearing loss was observed in all frequency domains on the right side.
Download Original Figure
3) 결과
우측 안면경련 증상은 호전되었으나 수술 직후부터 우측 청력 저하와 어지럼증을 호소하였고, 수술 3일 후에 진행한 순음청력검사상 우측의 모든 주파수 영역에서 현저한 청력 저하를 보였다(Fig. 6-b and 6-c).
고찰
BAEPs wave V 파형의 소실은 수술 후 청력 소실과 직접적인 연관이 있다[4]. 그리고, wave V 파형의 소실의 경우, wave I 파형이 보존되는 경우와 wave I 파형을 포함하여 모든 파형이 소실되는 두 가지 패턴이 관찰될 수 있다. 첫 번째 증례의 환자는 감시 중에 wave I 파형을 제외한 모든 파형이 소실되었고 수술 후 부분적인 청력감소가 나타났다. 이에 반해 두 번째 증례에서는 감시 중에 wave I 파형을 포함한 모든 파형의 소실을 보였고 수술 후에는 완전 청력소실과 어지럼증이 나타났다. 실제로, wave I 파형이 보존되었을 때보다 wave I 파형을 포함한 모든 파형이 소실되었을 때 청각 소실과 다른 합병증들이 더 빈번하게 나타났다는 선행 연구가 있었고[5], 본 증례에서도 이에 합당한 소견을 발견할 수 있었다.
일반적인 미세혈관감압술 과정 중 주요 절차인 테플론 패드 삽입, 소뇌 견인 등에 파형의 변화가 가장 많이 발생하여 이 시점에 감시를 집중적으로 진행한다. 그러나, 세 번째 증례에서는 주요 절차 중에는 파형의 변화가 없었고, 경막을 닫고 수술을 마무리하는 과정에서 모든 파형이 소실되며, 환자에게 수술 후 완전 청력감소와 어지럼증이 나타났다. 이는 주요 과정 중에 파형의 변화가 없더라도 지연성 변화가 발생할 수 있음을 시사한다.
BAEPs wave I은 가장 말단 부위인 달팽이 구역에서 유발된다[3]. 미세혈관감압술 중 BAEPs wave V 파형이 소실되었을 때 wave I 파형이 존재하면 전정와우신경 근위부의 외상성 기계적 손상을 의심하고 뇌 견인기를 제거하거나 와우 신경에 직접적인 영향을 미치지 않는 상태에서 기다리는 동안 식염수로 세척하면 회복될 가능성이 있다고 한다[5]. 주요절차 중에 wave I 파형을 포함해서 모든 파형이 소실되는 경우, 달팽이 구역에 혈액을 공급하는 내부청각동맥 및 관련 분지들의 경색, 연축 등 혈관 순환 장애를 고려해야 하며[6], 파파베린과 같이 혈관에 도움을 줄 수 있는 약물을 사용해서 회복될 가능성이 있다고 한다. 또한, 주요 절차 이후에 모든 파형이 소실되는 경우도 검사의 에러가 아닌 혈관 연축 등에 의한 지연성 변화를 시사하므로 따뜻한 식염수로 세척하거나 파파베린을 주입하는 등 순환 개선을 위해 적극적인 대처를 해야 한다고 한다[5].
결론적으로, 본 증례에서는 wave V 파형이 소실되었을 때, wave I 파형의 존재 유무 확인이 꼭 필요하고, 주요 절차 이후에도 파형의 변화가 생길 수 있으니 수술 종료 시까지 감시를 계속 유지하는 것이 바람직하다는 것을 보여준다.